Millwork & Interior Trim Glossary
A

Window Apron
Apron: A piece of the horizontal frame, window moulding or boxing, applied directly under the window stool on the wall; it also serves to hide the seal formed by the sill or the surface of the interior wall.
Architrave: Moulding installed on a window to increase the size; it also helps to hide the tabular lines.
Astragal: An internal moulding attached to two doors or an opening to prevent it from tipping over. Astragal provides a secure fit at the point where the doors. A flat astragalus is attached to the meeting stile of the door, and a T-shaped talus is at the approximate thickness of the swinging door.
B
Back Band
Back Band: A moulding with narrow grooves (notches) that are used in the baseboards and attached to the outer corner and outer edge of the interior window and the door box or on the floor for a rugged appearance of the panel. This increases both the ornamentation and the width of the filling.
Band Moulding: A flat, decorative or protective strip that flushes or extends above the surface; this moulding resembles a panel molding as well as an apron profile; It is usually used to cut mantels or cabinets.
Baseboard: This is also known as a wall base and is fixed along a finished floor at the bottom of the room.
Base Cap: A flush moulding with the wall in a piece of base moulding to create a decorative appearance. Sometimes it is used with the baseboard. The base cover can also be used as a panel or as a multipurpose.
Base Shoe: This is a narrow form, which is also known as a shoe or floor shape, forms the transition between finished floors and walls or cabinets. It protects the surface against damage and conceals irregular lines or cracks, where the surface meets the ground. The shape of the shoe can be used instead of a quarter turn.
Baluster: Vertical, spindle-shaped, square or turned stairs that carry a lane.
Balustrade: A system of railings and balusters, usually mounted on a staircase, balcony or landing, to provide protection and / or a handrail.
Bead Moulding: Smooth or hanging moulding are used when two surfaces meet at an angle. The profile usually consists of a pearl and a handle. It is often used instead of the crown, where the walls and ceiling meet.

Bow Window
Bevel: To cut at a different angle than a right angle, for example on the edge of a board or a door.
Bow Window: Three or more individual windows protrude out of the wall in a slightly curved outline.
Box Bay Window: A composite of three or more windows with side panels that protrude from the wall at a 90 degree angle.
Brace: It is used in an assembled window unit to maintain its squareness.
Breast: The dimension between the outer edges of the drawer or the pilasters of an entrance or shelf; Also "full width" of the layer.
Brick Mould: Thick moulding used in an exterior door and/or in an exterior window as a casing that connects the exterior cladding and provides a brick surface or other butt facing. It can be used to form a mesh screen, a storm protection belt or a combined door.
C
Cap – the top of an entrance, a fairing, a partition or a pilaster. Common Caps includes a dado cap, drip cap, entrance cap, e.t.c
Capital:The head, the crown or the highest structural element of a column, a pilaster or a pier.
Cap Moulding: moulding piece that is sometimes used in conjunction with a window or door ornament to illustrate the design of a simple ornament.

Casing (Window or Door)
Cased Opening: An interior opening without a door, but finished with poles and a box.
Casing: Trim used for door and window openings. The outer casing cuts the outside of windows and doors. The inner casing cuts inside the perimeter of windows and doors. Common casing includes door casing, exterior casing, head casing e.t.c
Caulk: Sealant for cracks and joints in door and window frames with waterproofing technique.
Chair Rail: Wall bar approximately 32 "above the floor and parallel to the pedestal. Originally, a railing was used to prevent the chairs from damaging the walls.
Column: A vertical structure of circular cross section composed of a base, a shaft and a capital; It can be a carrier and adornment.
Cope: Cut or shape the end of moulding so that it overlaps and corresponds to the outline of the part against which it is placed.
Corner Blocks: Square blocks used instead of mitering the side and main envelopes.
Corner Guards: Use corner protectors to protect the outer edges of a wall.
Cornice: The outer covering of a structure that adapts to the ceiling and the wall; It consists of boards and mouldings, namely, bed moulding, soffit fascia and crown moulding; it can be "boxed", "open" or "simple"; as well as the interior design to meet the roof and flanks; also the top part of the frame.
Cove Moulding: A moulded part with a concave profile allows smoothing the transition between two vertical planes. It can be used as a crown around the roof or in a vertical corner as corner protection. Also known as a moulding part with a concave profile, which is used mainly when two extremities meet at right angles; a rounded inner corner; in contrast to bullnose; also scotia, Cavetto, roof cornice.
Crown Moulding: It is also known as cornice moulding and it’s used to cover the intersection of walls and roof, usually from a large angle. The mouldings are always installed in suspension.
D
Dado: a rectangular groove cut in the grain of a wood leg; in contrast to the plow; which is cut with or

Dentil Moulding
parallel to the grain; with cladding the broad part just above the base.
Dentil Moulding: A moulding comprising of a series of small square blocks equally spaced and protruding as teeth.
Dentil Crown: Mouldings for crowns, consisting of teeth and other types of moulds, such as crowns and bases or base caps, to produce a mould system for crowns.
Doorjamb: The part of the frame of a door that surrounds and touches the edges of the posts and the top rail of a door.
F
Fascia: A wooden element that has appeared on four sides and is used on the outside of a "cornice" where it is stuck on the ends of rafters.
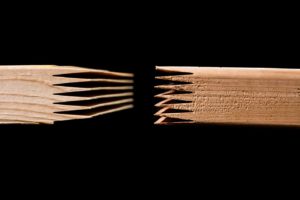
Finger Jointed Wood
Fillet: A narrow strip of wood between two slots in a wooden element; a flat, square moulding that separates the other mouldings; on the stairs, a thin and narrow strip of wood that fits in the helmet or intermediate plow between the balusters; sometimes "mould" of the neck.
Finger Jointed: A piece of wood with a series of fingers machined at the ends of the two parts to be assembled, which are coupled together and held in place with a water-resistant adhesive.
Flat Stock: Finished 3 or 4-sided boards for use on shelves, window frames, pedestals or pedestals.
Frame: All pieces that surround the window or the door; the vertical elements are called lateral pillars, the upper horizontal part is called head jamb and the lower horizontal part is called the sill.
Full Rounds: Carpentry in the form of rods, which is used as closet poles, curtain rods and/or towel rails.
H

Hardwood
Hardwood: One of the botanical groups of trees whose leaves are broad in contrast to the needle-shaped leaves of conifers or conifers; hardwoods are (1) deciduous (they lose their leaves in autumn or at the end of each growing season), (2) they have shorter wood fibers than conifers, (3) they contain cells (containers) with a diameter relatively large (in addition to wood fibers) and (4) have seeds that are surrounded by an ovary.
Header: A horizontal structural element (also called "lintel") that carries the load in an opening such as a window or door.
Heel (of a door): The “hinge” edge of a door.
Horn: The extension of a stile, sill or jamb. Various types of horns are the double horn, jamb horn, sill horn and stile horn.
J
Jamb: A vertical peripheral frame of a window or door. The most common size for indoor use is 1-1/16 inches thick and 4-9 / 16 inches wide.
Joint: To join two pieces of wood with nails, glue, adhesives or other means; can be connected end to end, edge to edge, end to end or end to end; also glue or wood stamp. Common types of joints includes blind mortise and tenon joint, butt joint, coped joint, dado joint e.t.c
K
Kitchen Cabinet: A box or box-shaped arrangement comprising doors, drawers and shelves, which are mainly used to store food, utensils, clothes, cleaning equipment and the like. Common types of kitchen cabinets are base corner cabinet, base end kitchen shelf unit, built-in kitchen cabinet e.t.c.
L

Lambs Tongue Moulding
Lambs Tongue: A moulded part with a considerable protrusion with respect to its width of two opposite pallets separated by a fillet.
Lattice: Thin strips of PVC or woven wood coated on four sides.
Lineal Foot: A foot of a moulding, independently of its width or thickness, also called the running foot; this term generally refers to unspecified lengths. Just to have length; Use in the amount of moulded parts; The "linear" foot generally refers to unspecified lengths.
Lip: On the edges of the door or the drawer of a cabinet there is a slot that extends in a closed position on the front or the surface of the cabinet. a rounded edge hangs over.
M

Interior Millwork
Mantle: Cover a fireplace with wood, stone, marble, bricks or similar materials and generally with a plate or shelf that protrudes above it; piece of mantel.
Millwork: A term used to describe products made mainly of sawn wood in a planing mill or in a carpentry plant; Includes mouldings, door frames and entrances, shutters, frames and windows, doors, stairs, kitchen cabinets, shelves, porcelain or corner cabinets; Wood crafts.
Miter: An incline cut at the end of a linear part, which is normally used to join an equally cut part to a corner. A tail cut at a different angle from a right angle.
Moulding: A narrow strip of curved wood used to accentuate and emphasize the ornamentation of a structure and to conceal surface or angled joints. The moulding can be exterior or interior.
Mullion: It is also called mull. A mullion is the vertical element of a frame, window or door frame between openings in a multi-window frame.
N

Newel Cap
Newel: The main post at the beginning of a staircase and the rigid post at the landing; a new staircase. The current types of newels are landing newel and starting newel.
Newel Cap: A crooked decorative cap or lid into which the dowel or pin of the newel is inserted.
Newel Collar: A twisted wooden collar that extended the base of some new stair newels.
P

Panel Moulding
Panel Divider: A moulding that separates two vertical wooden panels along their common edges.
Panel Mould: Decorative mould for the construction of elevated panels for walls.
Picture Frame Moulding: A narrow mould along the perimeter of the walls near the roofline to hold the hooks when hanging pictures. It can be used to make decorative and formal squares on the wall.
Plinth Block: A decorative wooden block that is thicker and wider than a door frame and used as a door ornament on the base to enhance its appearance. The basic block is also known as a basic block, block of foot or block of the pilaster.
Plumb: Exactly perpendicular or vertical; at right angles to the floor of a structure.
Primed Moulding: Moulding with a layer of paint or primer applied to it.
PVC: a plastic material also called Polyvinyl chloride used to make moulding.
Q
Quarter Round: A moulding that corresponds to a quarter of the axis of a complete circle and can be used as a base shoe.
R
Rabbet: A groove cut on or near the edge of a piece of wood to fit the edge of another piece. This can be a rectangular recess or shape along the long edge of a piece of wood or cut along the end or edge of the piece of wood.
Rail: Horizontal member of an opening of the window or door. Common types of rails are bottom rail, center rail, check rails e.t.c.
Rosette: A decorative wooden panel used at the intersection of two materials, attached to a wall and adjacent to the end of a railing. It can also be used as decoration in the lower part of the windows or doors.
S

Kitchen Soffit
Scallop: A decorative wooden element that contains a series of curves or zones of sawn circles or formed in one of its edges; a scalloped member.
Scotia: A deep concave shape of more than a quarter of a section; behind the bull; creek moulding.
Screen Mould: It is traditionally used to keep sifting in a wooden frame. It is also suitable for edges or wooden wallpaper.
Soffit: The bottom of the cornice; in kitchens, the ceiling lowered just above the top of the cabinets, which insulates the cabinet space too high to be used; known as "suspended ceiling”.
Softwood: One of the botanical groups of trees with evergreen leaves in the shape of a needle or dandruff; softwoods are evergreen (only three of the main indigenous species are deciduous), have fibers longer than hardwoods, contain no vessels and have bare seeds; Also known as "cone bearer" or "conifer".
Solid Moulding: Nonfinger jointed moulding.
Square Foot: A unit of measurement that equals a square and measures one foot on each side.
Stool Moulding: Interior trim element that serves as a frame for a window sill or window frame and is usually covered with rabbeting.
Stop Moulding: In the case of window trims, a moulded part that holds the frame of a double-wing window and can also be used as an apron under the window stools.
T

Interior Trim/Moulding
Trim: Carpentry, mainly shelves and / or carpentry for the finishing of door and window openings, chimneys, walls and other elements. Common types of trims are running trim, standing trim and side of trim.
W

Painted Wainscoting
Wainscot: The Lower surface of the inner wall that rises from the surface of the upper wall and usually has a height of 3 to 4 feet, often with a chair rail mounted on its upper periphery and a base around its lower periphery.
Wainscot Cap: A final piece for the top part of the wainscoting. Can be used with a chair rail to create a wider profile.
Wall Base: A moulded part that is placed along a finished floor around the circumference of a room.
Window Trim: Mouldings and / or trims needed to complete or finish a window frame.
Woodwork: Used synonymous with Millwork; It can be applied to anything that is made of wood.
